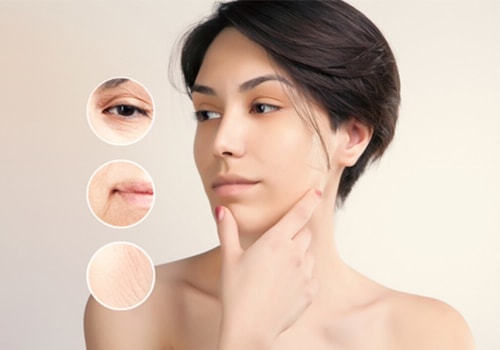
These amino acids are grouped together in a form known as a triple helix, and that's what makes up collagen. For this triple helix to form, you need to have enough vitamin C, zinc, copper and manganese in your diet. Vitamin C has already been added to many collagen supplement formulas (such as Reserveage Collagen Replenish), but you can also take your collagen along with a vitamin C supplement or C-rich foods like citrus, peppers, broccoli, or strawberries to reap the benefits, Axe says. The downside of collagen protein, although minor, is that unlike whey, hemp and soy protein, collagen isn't a “complete” protein, meaning it doesn't contain all nine of the 20 essential amino acids our bodies need to build protein and function, explains dietitian Jonathan Valdez, R, D, N.
In addition, the levels of these amino acids in collagen are not as balanced as in protein supplements made from complete proteins. Hyaluronic acid is found together with collagen in the body's connective tissues and helps to link collagen with another protein, elastin, which stretches the skin, explains Valdez. Since hyaluronic acid also has moisturizing properties, a lack of it can result in dull, dry, and lifeless skin. That's why you'll find it in serums and lotions in the beauty aisle.
If you're feeling creative, try mixing a spoonful of collagen peptide powder with mashed avocado for an improved version of avocado toast. However, he is now curious to know how collagen intake affects his daily life, in particular with the daily supplements he already takes, such as a multivitamin, vitamin D, magnesium, vitamin C, fish oil or others. The more you add to a collagen supplement, the more uncontrolled chemical reactions can reduce the bioavailability of all the nutrients involved. Vitamins that have an antioxidant effect can also act as prooxidants, and these prooxidants can oxidize the amino acids in collagen.
In other words, taking high amounts of vitamin C with collagen could be counterproductive, according to Dr. Some products claim that vitamins and minerals, such as vitamin C, magnesium and calcium, are necessary in collagen for absorption and maximum effectiveness. Why would they make such a statement? How many times have you seen this on a supplement label? Too many times to count, right? This tactic has a fancy name and is called product line extension. It's what a lot of supplement companies (and product companies) do to generate additional revenue.
The big collagen brands that use the product line extension are very interested in increasing profits. We introduce new products, to current customers, that have characteristics that, as humans, we know are intrinsically good (vitamin C, magnesium, prebiotics, etc.). It is well known that vitamin C is essential for the manufacture of collagen, it seems to be involved in every step of the manufacturing process, making vitamin C a vital molecule for skin health. Adding vitamin C to a culture of skin cells (fibroblasts) dramatically increases collagen synthesis.
Second, vitamin C is an antioxidant and can help reduce skin damage caused by free radicals. Therefore, when vitamin C is properly administered to skin cells, there is a good chance of reducing wrinkles and improving skin texture. The treatment for vitamin C deficiency involves replacing the vitamin C that is lacking in the diet; this can be achieved by taking vitamin C supplements and following a diet rich in vitamin C. Vitamin E's powerful ability to neutralize harmful free radicals has earned it the nickname of protector: it protects what enters and leaves the skin.
Experts consider vitamin E to be the most important antioxidant because, by protecting cell membranes, it prevents damage to the enzymes associated with them. Several studies have shown that applying vitamin E to the skin can reduce the damage caused by sun exposure; however, for additional sun protection, people may consider taking vitamin E supplements. Supplementing with 400 milligrams of vitamin E a day has been shown to reduce photodamage, wrinkles and improve skin texture. To include vitamin E in your diet, start including natural sources of vitamin E, such as vegetable oils, grains, oats, nuts, and dairy products.
Seeds and nuts that are especially rich in vitamin E. Certain minerals are also essential for collagen production. One of those minerals is copper; in fact, when the level of copper inside skin cells increases, collagen production increases. Copper activates an enzyme called lysyl oxidase, which is necessary for collagen maturation.
Active lysyl oxidase cross-links collagen fibers with other support fibers, helping to form the scaffold that supports skin and soft tissues. Because of its role in collagen production, copper also keeps bones, heart and blood vessels healthy. Copper also acts as an antioxidant, neutralizes free radicals and helps prevent them from damaging skin cells or tissues. Adults need 1.2 mg of copper a day, which should be available from a daily diet of healthy foods.
You can find copper in foods such as nuts, kidneys, crab, dried fruits, bran flakes, mushrooms, mussels, cashews, and squid. Keep in mind that copper is a potentially toxic metal, so supplements that contain more than the recommended daily dose of copper should not be taken. Zinc supports healthy collagen production by serving as a cofactor for collagen production, meaning it activates proteins essential for collagen synthesis. It also activates a protein called collagenase that allows cells to remodel collagen.
The amount of zinc you need is 5.5 to 9.5 mg a day for men and 4.0 to 7.0 mg a day for women. .